Clinical Conditions: Leg Length Discrepancy
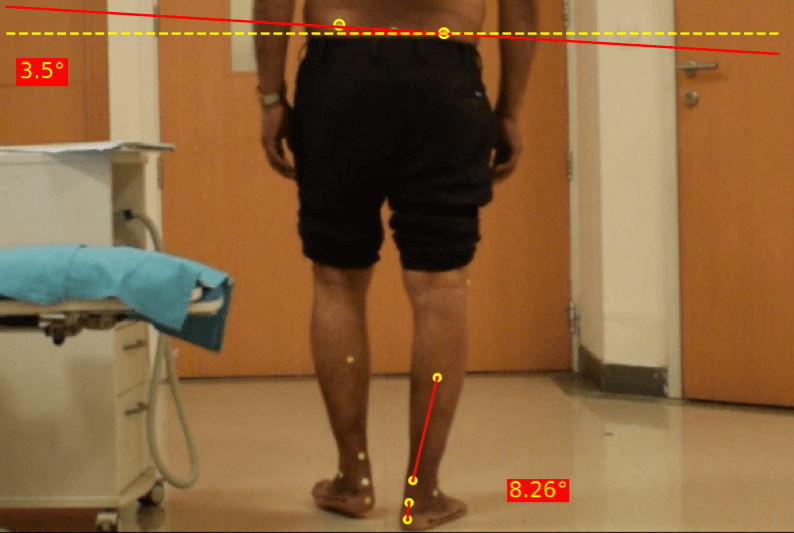
ABNORMALITY: The effect of an anatomical (structural) leg length discrepancy is most apparent during the single support phase of the shorter side. During this phase, the contralateral pelvis is hiked to allow the longer leg to pass through. The pelvic hike may also accompanied by a compensatory lateral bend of the trunk.
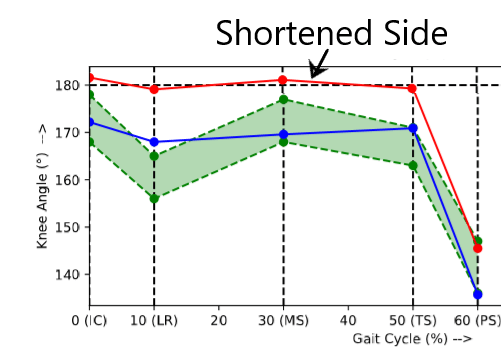
In addition to the ipsilateral pelvic drop, some patients try to increase the effective length of the shortened leg by exhibiting excessive knee extension during the support phase of the shorter leg.
POINT OF OBSERVATION: Gait patterns for leg length discrepancy are best observed from the lateral view and the posterior view.
Resources for further reading
Note: The gait patterns described here are based on past researches. Please correlate all observations clinically.